
For this example, using 1.76 as the width would also work.

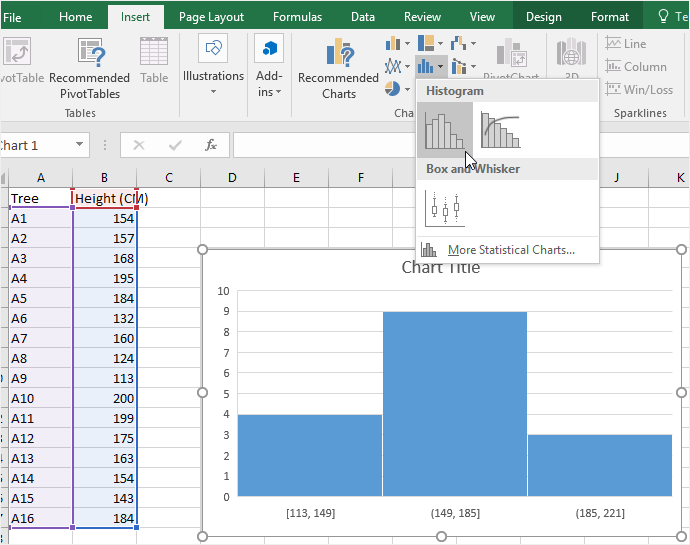
Rounding to the next number is often necessary even if it goes against the standard rules of rounding. Rounding up to two is one way to prevent a value from falling on a boundary. We will round up to two and make each bar or class interval two units wide. n = total number of data values (or the sum of the individual frequencies), and.(Remember, frequency is defined as the number of times an answer occurs.) If: The relative frequency is equal to the frequency for an observed value of the data divided by the total number of data values in the sample. The histogram (like the stemplot) can give you the shape of the data, the center, and the spread of the data. The graph will have the same shape with either label. The vertical axis is labeled either frequency or relative frequency (or percent frequency or probability).
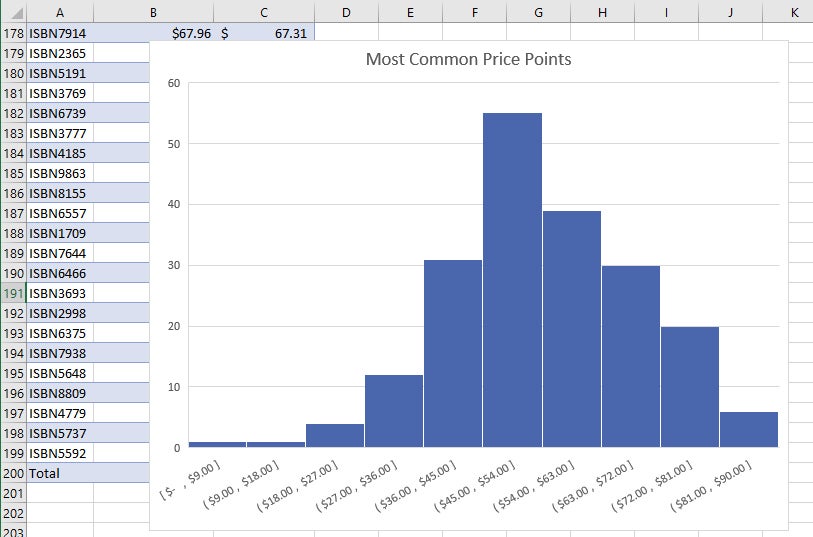
The horizontal axis is labeled with what the data represents (for instance, distance from your home to school). It has both a horizontal axis and a vertical axis. A rule of thumb is to use a histogram when the data set consists of 100 values or more.Ī histogram consists of contiguous (adjoining) boxes. One advantage of a histogram is that it can readily display large data sets. Recognize, describe, and calculate the measures of location of data: quartiles and percentiles.įor most of the work you do in this book, you will use a histogram to display the data.Display data graphically and interpret graphs: stemplots, histograms, and box plots.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
